Initial Public Offering (IPO)


Initial Public Offering or an IPO is one way through which a company raises funding to focus on expansion of the business. An individual can purchase the shares of a company as an investor.
There are several opportunities in the market for investment purposes and IPO is one of them: Let’s discover it. IPO is a great way for a company to raise capital for immense growth of the business. To achieve big milestones, the company raises funds from the general public. For an investor, they can hold a stake into a company and receive entitlements such as dividends and bonus shares.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is an Initial Public Offering (IPO)?

An Initial Public Offering – IPO serves the purpose of an investor as well as of the company that has issued its shares. If you want to start investing your funds in an IPO then let’s first understand it from the perspective of an investor:
How does IPO work for an investor?
An IPO gives an opportunity to the public to buy the shares and acquire a part of the company which can help the company to boost its capital. Let say, if you purchase any amount of shares in XYZ Company or an IPO, then you also own a part of the company.
Reasons to invest in an IPO

- Long Term Objectives: IPOs are the same as the investment in equity and can help you increase your wealth while achieving your long term objectives.
- Transparency: IPO’s offer transparency as they show the prices of securities which makes the complete procedure to be transparent. After the listing process, share prices are unpredictable due to market circumstances.
- Buy cheap and earn big: The prices of shares are discounted when a company goes public. It allows the investors to make an investment at lower prices as when the company gets listed, the shares are quite expensive.
Things to consider: Before investing in an IPO, all the sides must be analyzed briefly as it has both drawbacks and benefits. Some of the demerits of investing in IPO could be:
· It could hamper the privacy of an investor as some details have to be revealed.
· This could be time consuming as it is required to assess the performance of a company before making an investment.
· Impact of external interference may affect the pricing.
Eligibility to apply for an IPO: An investor must have a PAN card, a valid DEMAT account and have the ability to enter into a legal contract.
Also Read: New Fund Offer
How does an IPO work for the company?

With the help of IPO which stands for Initial Public Offering, a company can raise funds in the primary market by selling the securities to the public. It is recognized as a very important step to fuel the growth of a business. A company can raise funds with the help of these two methods:
- Fixed Price Issue
It is the price issued by the company to sell the shares to conduct their initial sale. Investors can know the price of the shares at which the company issues it.
- Book Building Issue
A 20% price band is offered on the stocks by the company that is going for IPO. In this, the investors can specify the number of shares and the amount they can pay per share as per their interest. Ultimately, the prices are determined by the bids of investors.
How can an IPO be beneficial for a company?
· Capital Access: IPO allows the company to obtain capital through substantial funding. It can give financial stability to the company by supporting it in research and development, paying off the debts, buying assets, etc.
· Business Credibility: A company ready to raise capital from the public has to comply with many rules and regulations as per the regulatory bodies which increases the credibility of the investors towards the company and hence increases their investment. It also helps to increase customer base, suppliers and partners.
· Debt Financing: Public companies have access to debt financing as compared to private companies.
· Increased Liquidity: The shares of the company are more liquid because of the IPO which gives easy access to shareholders to execute buying and selling of shares.
Know its limitations:
· Expensive Process: The process of IPO is quite expensive and complicated as the companies are required to pay hefty amounts of fees to the lawyers, accountants and investment banks.
· Regulation Compliances: There are various rules and procedures which need to be followed before going public which can be very time consuming and costly.
· Dilution of shares: Shares are diluted as new shares are issued by the company reducing the value of existing shareholders stakes.
Terminologies associated with IPO

| Stockbroker | Stockbrokers or broking firms allow investors to apply for an IPO. Investors can purchase and sell their shares with the help of stockbrokers. |
|---|---|
| Bid Lot | Lots are pre determined by the companies and the investors are required to purchase the minimum number of shares which is called a Lot, as defined by the company. |
| Floor Price | Minimum bidding price set by the company when applying to an IPO. |
| Issue Price | It is the price at which the shares of a company are sold when they are first available to the public. |
| Cut Off Price | The shares are allotted to the investors at cut off price. |
| Abridged Prospectus | Abridged prospectus contains all the salient features of IPO issues. It is mandatory to attach an abridged prospectus for the companies while filling an application for an IPO. |
| Anchor Investors | Qualified Institutional Buyers (QIB) includes investors such as banks, mutual funds, financial institutions, etc. Under this category, 60% of shares are reserved for the anchor investors who apply for shares worth Rs 10 crore or more in the IPO. |
| Draft Red Herring Prospectus | An offer document containing complete financial and operational details about the company is called Red Herring Prospectus (RHP). It is issued by the company with SEBI and the Registrar of Companies before the commencement of IPO process. |
| Listing Date | After the completion of the allotment process, trade can be executed in the secondary market when the shares are officially listed on the stock exchange. |
What is the process of IPO?
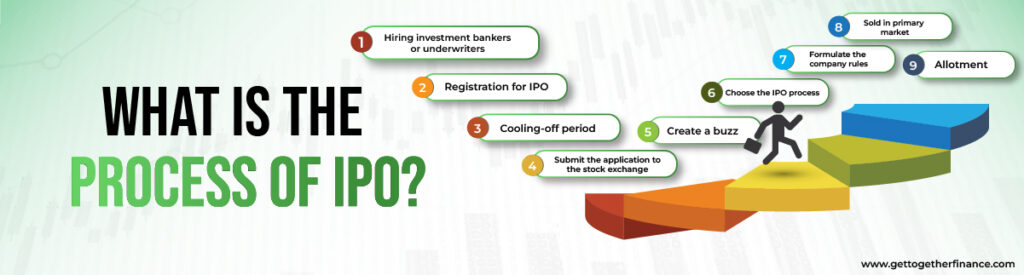
It is a very complex process for any business that has decided to go public. This process may take from six months to nine months. A company has to follow the given steps:
Step1: Hiring investment bankers or underwriters:
Financial experts guide the company to carry out the whole IPO process.
Step 2: Registration for IPO:
The companies register through a document called red herring prospectus. It is a formal procedure which must be completed by the company and disclose all the vital information of the company as guided by SEBI.
Step 3: Cooling-off period
SEBI conducts the verification process by looking for errors and discrepancies and approves the date for an IPO.
Step 4: Submit the application to the stock exchange
To conduct the initial issue, the company should file an application with the stock exchange.
Step 5: Create a buzz
People should know about the IPO of a company so the company has to ensure that they convince the investors. For this, various events are organized with the help of which IPO of the company is at the hype.
Step 6: Choose the IPO process
The company has to make a choice among fixed price issues and book building issues.
Step 7: Formulate the company rules
Before launching an IPO, business must make sure that no insiders trade in the IPO to maintain the efficacy.
Step 8: Sold in primary market
To conduct the final stage, the shares issued are sold in the primary market and money is collected from the investors. The bidding can take place for approximately five working days. When the bidding is done, IPO shares are allotted to the investors within the next 10 working days.
Step 9: Allotment
The last step is the allotment when the shares are allotted to the bidders. This is the last step where the company identifies the total number of shares allotted to each investor. Partial allotments are made if there is a case of oversubscription.
Some Successful IPOs are:
- ICICI Lombard: Insurance Giant – Commencement of trading at Rs 70 which provided nine fold returns in 2017 at Rs 680 per share.
- Lux Industries – Commencement of trading at Rs 75 in 2014, nine times returns were provided within a year at Rs 735 per share.
- ICICI Prudential– Commencement of trading at Rs 70 in 2011, four-fold returns were provided in 2016 at Rs 350 per share.
Conclusion
As we have understood, companies raise funds through the public by getting listed into the National Stock Exchange or other representatives with the help of Initial Public Offerings. It depicts the starting phase of a company into the stock market.
FAQs
Q1. What is an IPO?
Initial Public Offering (IPO) is when a private company decides to go public by selling its shares which indicates the ownership of shareholders.
Q2. Is investing in an IPO risky?
When investing, there are some sort of risks involved with stock as well as IPO’s. Investors need to analyze the risks properly and make informed decisions.
Q3. How can I apply for an IPO?
Get in touch with a broker or an entity to apply for an IPO.
Q4. Can I make profits by investing in an IPO?
You can make good profits by investing in an IPO. You can surely gain profits by investing in an IPO if the company does well in future.



 Facebook
Facebook Instagram
Instagram Youtube
Youtube
