From Government to Corporate: All About Different Types Of Bonds

In India, the history of first borrowing goes back to 1867 for railway construction. Although, the interest rate of bonds varied in India from time to time. In 1857 it came down to 5%, later gradually falling to 4% in 1871. Apart from that, during the first world war, a rise in public debt was also encountered.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview
Long time ago, in 1860, bonds announced their arrival in the world of finance. With time, they have become super popular with all sorts of types. But why, you ask? Well! Because of their irresistible cool features that everyone loves. They provide a steady stream of cash, ensuring investors receive their interest payments on time. It is like having a piggy bank that never runs out. They are like your money buddies and the best part? There’s a whole bunch of them, each with their own specialty.
Without further ado, let’s get right into the blog of bonds and different types of bonds.
What Is a Bond?
In the world of finance, bonds are like special deals (agreement) where one party owes money to the other party. The one who owes the money is – the debtor – promising to pay back the borrowed amount. The borrowed sum of money is known as PRINCIPAL – to the bondholder when it matures, which is a specific future date.
Oh, and there’s more – the debtor also agrees to pay interest, or as they call it, the coupon, over a specific period. The difference in the amount and timing of these payments leads us to different types of bonds. And guess what? The debtor often gives the interest at regular intervals, like annually or every six months.
In simpler terms, a bond is an agreement that allows someone to borrow money, helping in raising funds for their projects, or in the case of government bonds, to cover ongoing expenses.
Different types of bonds
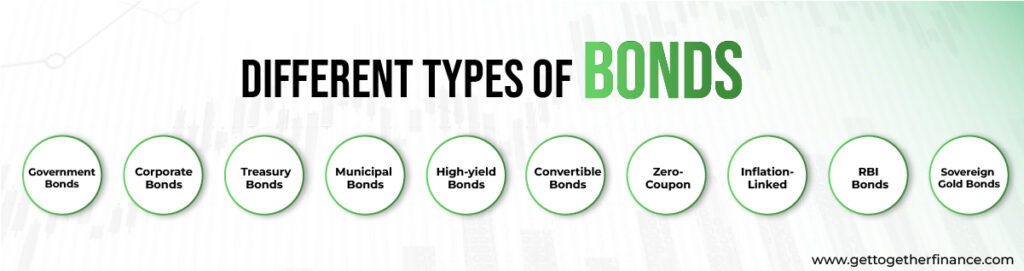
Now it is safe to assume that you are well aware of the basics of bonds, but there is much more to the story. There are numerous types of bonds, each of them serving different purposes. Let’s dig deeper without wasting any time
1) Government bonds
Government bonds in India are just like giving a helping hand to state or the central governments, especially during the times of liquidity crisis for hefty projects such as roads and buildings. What’s on the table? Well, they promise to repay the principal amount with the set interest, and it’s all set to happen on a particular date. These bonds are counted under the long-term investment category, known as government securities (G-Sec), lasting about 5 to 40 years.
Remember those state-government bonds we discussed earlier? They perfectly fit into this category too, going by the name State Development Loan. Initially, it was like an exclusive club for big-shot investors, but guess what? Now, even regular investors and small banks can get in and access government bonds. It’s a bit like putting your money into an account where you get a sweet little extra every six months – almost like a bonus for being a savvy saver.
2) Corporate bonds
These are types of loans that companies take from regular people like you, to fund projects or handle the company’s everyday costs. Let’s break it into a simpler way, when a person buys a bond, they are lending money to the company, which pays them back with extra money called interest. The company pays you back with a little extra, known as “interest.”
In India, there are different types of bonds of corporate based on factors like risk, connection to company ownership, and how well they handle interest payments. One can say that corporate bonds help carve a path or a way for them to support a company and earn a little extra money out of it.
3)Treasury bonds
Let’s talk about Treasury bonds – the superheroes of safety in the bond world. Why? Because they come with the minimal to no risk. Let’s talk about Treasury bonds – the superheroes of safety in the bond world. Why? Because they come with minimal to no risk. When the government issues these bonds, you can rest easy because there’s zero chance of them not paying you back. But what’s the tenure? It is a solid ten to thirty years, and here’s the sweet part – they offer a fixed interest rate. This rate, of course, dances to the tune of the current market conditions. So, with Treasury bonds, it’s like a secure ride with the government at the wheel. No worries, just steady returns.
4) Municipal bonds
Let’s talk about the community champions of the financial world – municipal bonds. State and local governments use these funds for crucial works such as building schools or hospitals for the community. Here is the cool part! People who meet the criteria may earn a tax-free income from these bonds. But what’s the catch? The interest rate is usually lower compared to other bonds. It’s a bit a trade-off, but you are contributing for the good of your community!
5) High-yield bonds
Time to talk about high-yield bonds, also known as Junk Bonds. The speciality of these bonds are that they come with higher interest rates, but here’s the deal – with great returns come great risks. In comparison to safer investment-grade bonds, Junk bonds are a bit riskier due to their lower credit ratings. That means more interested investors, right! You’ll often find these bonds in the hands of startups or companies shouldering a hefty load of debt.
If broken down into simple terms, high-yield bonds are like risk-takers in the investment game. They’re open to more risk, but in return, there’s a chance for higher returns. It’s an appealing option for those who want to earn huge, even if there’s a higher chance that the issuer might struggle to pay back the debt.
6) Convertible Bonds
Let’s talk about the elephant in the room! Convertible bonds are like the chameleons of the investment world – combining both debt and equity features. In bookish terms, these are a type of hybrid security which starts off as a normal regular bond, which pays periodic interest.
But what sets it apart is the convertible feature. Bondholders can transform their bonds into a specific number of common stocks from the issuing company, within a predetermined time or under certain conditions. Once the bond is converted, you officially become the shareholders of the company.
Why do people dig convertible bonds? Well, they bring a sweet level of flexibility. Investors can select between the stability of debt and the growth potential of equity, as per the market conditions or their investment game plan. It’s like having the best of both worlds!
7) Zero-Coupon
The rebel of the bond world! Unlike regular traditional bonds that pay periodic or timely interest, zero coupon bonds don’t give any interest payment throughout its whole tenure. Instead, they are issued at a price lower than their face value that’s why they are also known as pure discount bonds. In simpler terms, it is initially sold at a discounted price to its face value.
Now you must be thinking about what good it does for normal people. The return on investment rolls in when the bond matures. That’s where the investor gets the face value of the bond which is usually higher than what they paid. The difference between purchase price and face value is the interest earned over the bond’s entire tenure.
8) Inflation-Linked
Inflation-linked bonds – the superheroes that shield your investments from the pesky impact of inflation. Basically, the government of the country issues these bonds. The interesting factor – both the main amount and the interest rate change or fluctuate on the basis of how much prices are going up. For example, if inflation goes up, the amount you invested and the interest also goes up with the inflation. This helps in protecting your money from losing its value and making sure that your investment aligns with the rising cost of living.
9) RBI Bonds
The cool bond- authorised by the RBI, specifically the FRSB (Floating Rate Saving Bonds) 2020 – also known as RBI taxable bonds. This bond has a lifespan of seven years during. The interest rate is not fixed but actually fluctuates on the basis of market conditions. FRSB adjusts and pays interest every six months rather than giving it on maturity.
10) Sovereign Gold Bonds
Now here comes one of the most popular bonds: GOLD BOND, these bonds came into play by the authority of the central government. It is mostly suitable for those who want to invest in gold but do not want to keep the gold in physical form, it’s like having something precious but not having to worry about it.
The plus point of this bond apart from not worrying about the gold is that the interest is tax-free!! Yes, whatever interest you will earn from this bond will be exempted from tax. Apart from all the different types of bonds, gold bonds are considered highly secured bonds as it is offered by the government.
Also Read: What is Bond Yield
How To Invest In Different Types Of Bonds In India.

If you are thinking of investing in financial instruments or tools like bonds, you either trade in the primary market or in the secondary market. In the primary market, issuers first sell their bonds to investors to raise funds. On the other hand, in the secondary market, these tools or instruments are actively traded on exchanges. Generally, these types of bonds are considered less liquid and often held until maturity.
In today’s time, even small investors have easy access to purchase government bonds. Acquiring government bonds in India has become easier and more accessible through platforms such as brokers.
Limitations of Bonds
Despite the many cool features bonds offer, they also have some limitations.
Interest Rate Risk
Usually when the interest rate touches the sky, bond prices tend to go down. This means that if an investor has to sell their bonds before the maturity period, they might end up selling them for less than what they paid. Risk becomes more significant when the overall interest rate gains a new rise.
Inflation risk
Although bonds provide a steady flow of income, inflation can degrade the value of that income over time. This means investors can face certain losses and may end up with less purchasing power.
Liquidity risk
Bonds can be difficult to sell sometimes, specifically if they are not traded frequently. It can be quite a problem for investors who must sell their bonds before maturity.
Conclusion
To conclude it, there are different types of bonds, though we have only covered 10 of them, they give investors numerous options to manage their money. Understanding these bonds types can help investors to make safe and sound decisions in building strong and diverse investment plans to reap the benefits. However, it is crucial to understand the in-depth insights of the bonds you opt for and seek legal advice before making an investment.
FAQ
When did the concept of bonds first emerge in India?
In the Indian terrain, bonds first came into the picture in 1867 for raising the funds for railway construction. Apart from this, during the First World War, the public debt deepend, raising a concern. The interest rate of bonds changed with time. For instance, in 1857, it was dropping down to 5$% and gradually to 4% in 1871.
What is the fundamental concept of a bond in finance?
In the land of finance, different types of bonds play different role of a special agreement where one party lends money to another. To record the exchange, a contract is placed, promising to repay the borrowed amount (principal), along with interest (coupon) on pre-determined dates. Although, not all types of bonds can be traded easily and not all securities are available to private sectors.
How do government bonds in India contribute to infrastructure development?
Government bonds in India open opportunities to investors for lending money to central and state governments. Such contracts are needed, especially during the liquidity crisis, for massive projects such as infrastructure, roads, or buildings projects.
How did the interest rates of bonds evolve in India during the late 19th century?
In 1857, interest rates were at 5%, gradually decreasing to 4% by 1871.
What are the characteristics of corporate bonds and how do they differ from government bonds?
Corporate bonds are basically the money borrowed by companies from investors/individuals. They fund projects or cover everyday costs, and they vary based on risk level, ownership connections, and interest payment handling.
Why are treasury bonds considered the safest bond in the market?
Due to minimal risk of default. Yes, treasury bonds are considered the safest by the government, making the risk of them not paying back a little laid back. They stick around for ten to thirty years and offer a fixed interest rate.
How do municipal bonds contribute to community development?
The creamiest of all! Municipal bonds are a way for local and state governments to raise funds for projects like schools and hospitals. The investors get the added benefit of tax exemptions if you qualify.
How does a convertible bond differ from a regular bond?
Chameleons of the bond world – convertible bonds. They combine features of both equity and debt. Initially, its functions started off as regular bonds but you get the choice to convert them into a specific number of common stocks of the issuing company under certain conditions.
Why are Sovereign Gold Bonds considered as highly secure?
Sovereign Gold bonds act like your gold guardian angels, offered by the central government. They are considered as one of the most secure options for individuals who want to invest in gold but don’t have the hassle of storing it physically. Plus, the interest you earn is tax-free!
How can you invest in different types of bonds in India?
Easy process! You can explore your options of bonds in India in two ways – snagging Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) of big companies in the primary market. Or you can directly explore the options of the active trading scene on exchanges like the National Stock Exchange (NSE) in the secondary market.



 Facebook
Facebook Instagram
Instagram Youtube
Youtube
