Dividend: Understanding Stocks Dividend and How They are Paid
- June 20, 2024
- 1904 Views
- by Manaswi Agarwal


A dividend is a payment in the form of a reward that is offered by a publicly listed company to investors who own the stocks of the company. The source of dividend is the company’s net profit which is extended to the shareholders in the form of cash, cash equivalents, shares, etc. The rate of dividend is decided by the company’s board of directors from the remaining share which has been earned by the company. A dividend is a regular payment of profit to the shareholders.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is the Dividend?

In order to retain shareholders and improve the company’s reputation, a firm regularly pays dividends to its shareholders in a form of reward for investing in their company. A dividend can be paid to the shareholders in the form of cash, cheque or many other forms as decided by the board of directors. Generally, dividend is paid from the extra earnings made by the company in the financial year which depicts a sound financial position of the company with a consistent growth. Moreover, shareholders prefer to buy dividend paying stocks as dividends are distributed by well established companies that results in keeping their investments safe.
Types of Dividends
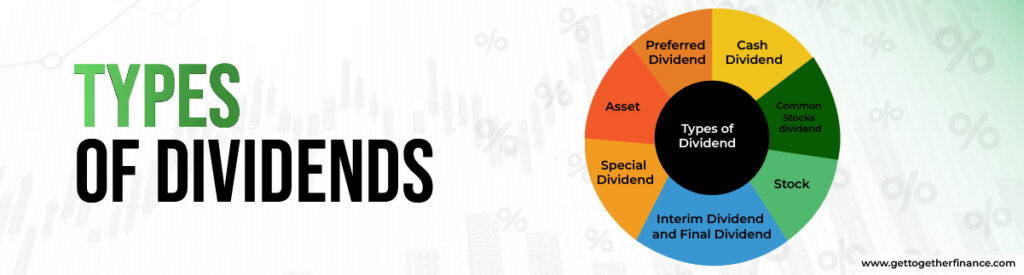
A company can pay reward to the shareholders by offering those shares of a new company, warrants, and assets as well. The dividend paid to the shareholders has the potential to influence the company’s share price accordingly. There are many other ways in which a company can declare dividend, let’s get to know them:
Special Dividend
Special dividend is paid to the investors on a common stock which is often issued under special circumstances like when a company has accumulated substantial profits over several years. These dividends are paid from the profits that are looked upon as excess cash which is not to be used by the company in near future.
Preferred Dividend
Preferred stock owners are eligible to receive preferred dividends as it accrues a fixed amount which is paid on a quarterly basis to the shareholders.
Interim Dividend and Final Dividend
During the financial year which is from April to March in India, an interim dividend is announced by the companies before the preparation of the final full year accounts. So the interim dividend is declared by the company on a yearly basis. On the other hand, the final dividend is declared after the accounts for the year are finally prepared.
Cash Dividend
The payment is made to the shareholders in the form of cash by the company. This is the most common type of payment where the payment is usually made electronically or can be paid by cash or cheque.
Asset
Apart from cash, some companies can reward shareholders in the form of physical assets, investment securities and real estates. Though it is not a common practice still many companies tend to do so.
Stock
Stock dividends are paid to the shareholders by issuing new shares. The stock dividends are distributed on a pro-rata basis where each investor can earn the dividend depending on the number of their holding shares.
Common Stocks Dividend
The dividend is paid to the common stockholders from the accumulated profits earned by the company. The amount of dividend is often decided by the law when the company decides to pay its dividends in the form of cash.
How to calculate dividends?

To calculate the dividend, dividend payout ratio is calculated where annual dividend per share is divided by earnings per share. Dividend payout ratio helps to identify the amount of money a company might offer to its shareholders, a company with a steady dividend payout ratio represents robust financial growth.
Dividend Payout Ratio = Dividend Paid / Reported Net Income
Dividend Per Share
Dividend per share is calculated by dividing the number of dividends paid by the company by the total number of shares held which is described as:
Dividend per Share (DPS) = Annualized dividend / Number of outstanding shares where,
Annualized dividend = Quarterly Dividend Amount * 4
Weighted Average Outstanding Shares = (Outstanding shares in beginning + Outstanding shares at the end) / 2
Let us understand this by an example:
If a company declares a quarterly dividend of Rs 50 lakhs then the annualized dividend amount = 50*4 which is 200 lakhs.
If a company is predicted to have 80 lakhs shares in the beginning and 120 lakhs shares at the end then the count of weighted average shares is 80+120 = 200/2 = 100 lakhs.
Therefore; the dividend per share is = 200 / 100 = Rs 2.
Impact of Dividends on Share Price
The activity of rewarding dividends positively impacts the stock prices in the market which cause a surge in the prices. A premium price is to be paid in order to earn dividends. Once the dividend is paid to the shareholders, the move cannot be reversed. Due to the reaction of market activities, an up move is experienced in the share prices but the prices start to decline by a similar proportion when the date of dividend eligibility expires. The fall in prices is observed when new investors are not eligible to receive dividends and are reluctant to pay the associated premium.
Dividend Yield
Dividend yield is a ratio that depicts your income earned in dividend payouts per year for every penny that is spent in a stock, a mutual fund, or an exchange traded fund (ETF). In other terms, dividend yield is expressed as a percentage of the current price of a stock’s annual dividend payment. Dividend yield tells you about your annual return on investments according to the price you have paid for the security. Dividend yield is essential to understand because you can significantly boost your returns by reinvesting your dividends. You can calculate this by understanding the company’s fundamentals and conducting research through resources and websites.
Dividend Paying Stocks
Companies that are well established and are able to generate regular profits are the best dividend payers and maintain a good record of dividend payments. Some sectors that have been constantly performing well in paying dividends include basic materials, oil and gas, banks and financial, healthcare and pharmaceuticals and utilities. You can go through this blog to know about the best dividend paying stocks.
Advantages of Dividend

The strategy of investing in dividend stocks where the investors focus on investing in stocks that pay regular dividends. These stocks have several benefits to the investor where they can make extra income from dividends apart from their investments.
Consistency
Dividend paying companies provide a consistent stream of income to their shareholders which reflects its historical stability and these companies tend to be more stable and mature as they hold a long record of profitability as well as cash flow generation.
Passive Income
Investment is a great source of passive income for investors where dividend paying stocks are additional benefits to boost the capital. Dividends are rewards received by the investors for which they are not required to take any extra efforts.
Portfolio Diversification
Investors can invest in a wide range of sectors to diversify their investment keeping it safe at the same time. This helps to maintain the portfolio effectively as spreading investments into various dividend paying stocks would ultimately result in capital appreciation.
Growth Potential
Many dividend paying stocks are associated with well established companies which are expected to grow in future also increasing their dividends over time. Investors have the opportunity to potentially increase their income by earning compounding returns and creating wealth over the long term.
Tax Benefits
Tax on dividend is at a lower rate as compared to other sources of income. Investing in stocks that pay dividends offers tax benefits as they do not have to pay huge amounts of taxes.
Compounding Returns
Investors can generate compounding returns which means they can have multiplied returns on their investment by investing in stocks that pay dividends.
Here are some advantages of paying dividend for the companies:
Investor Attraction: A company that pays a dividend implies that it is stable and can generate sufficient profits to pay the investors. A company with sound financial conditions attracts investors which enhance its shareholders base.
Efficiency in Capital Management: A company can efficiently manage its surplus cash by paying it as a form of reward to the shareholders.
Brand Loyalty and Reputation: Regular dividend payments enhance company’s reputation among the investors and creates brand loyalty in the eyes of investors encouraging them to invest more.
Also Read: Primary and Secondary Markets
Conclusion
Dividend is a reward earned by the shareholders who have invested in the company. A dividend paying company is well reputed in the eyes of investors as it generated extra income for them. To know about where to invest, GTF offers a well built technical analysis theory based on Demand and Supply zone which has proven to be one of the most reliable ones through which investors can generate sufficient amounts of profits.
FAQs
What is the Dividend in Stock?
Dividend is paid by a company to its shareholders as a reward for their holdings. Through dividends, investors can earn a certain amount of regular returns from investing in stocks.
How is the Dividend Calculated?
Dividend is calculated by dividing the entire number of dividends paid by the company by the total number of shares held by the shareholders.
How is a dividend taxed in India?
In India, a company must deduct the tax at the rate of 10% from dividends if the amount distributed to the shareholder exceeds Rs5000.
What is Dividend Yield?
Dividend yield is calculated in the form of ratio or percentage where the total income earned through dividend payouts per year is calculated for the investor based on the amount you have invested in each stock.



 Instagram
Instagram
