Fiat vs. Crypto: Understanding the Key Differences
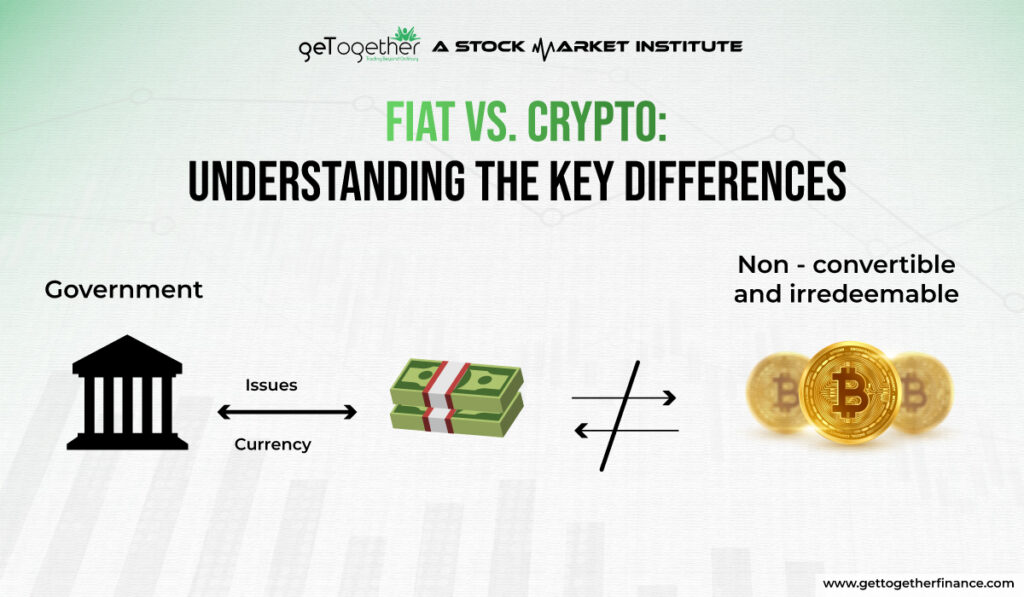
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview
Digitalisation has transformed the world and a cashless society is what we see in the modern world. So far, even with the traditional currency remaining the face of a country, the money is exchanged electronically through online wallets, payment apps, debit cards, etc.
Earlier in 1971, the US initially changed the gold standard and introduced its fiat currency, the dollar. Now the question emerges of how the future looks at cryptocurrencies and how they differ from fiat currency. This blog will study the basics and history of government-backed currencies as well as digital cryptocurrencies to establish the key differences between fiat currency vs cryptocurrency.
What is Fiat Currency?
Fiat currency is a type of money that is issued by a government and holds value because the government maintains it and people have faith in its value. Unlike commodities like gold or silver, which have intrinsic value, fiat money doesn’t have value on its own. Its value comes from the trust and confidence that people have in the government that issues it.
Overall, fiat currency remains the dominant form of money globally. It facilitates trade, serves as a unit of account, and allows for storing value. However, with the rise of digital technologies, cryptocurrencies are emerging as a potential alternative.
Examples of Fiat Currency
Indian traditional fiat money is the Indian Rupee (INR). Besides, common examples of fiat currencies include the US Dollar (USD), the Euro (EUR), and the Japanese Yen (JPY). These currencies are used for everyday transactions like buying groceries, paying bills, and earning wages.
The Role of Central Banks

Central banks play a crucial role in the management and regulation of fiat currency in any country. In India, this role is fulfilled by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Here’s an overview of how the RBI manages fiat currency in India:
Issuance of Currency
The RBI is the sole authority responsible for issuing currency in India. It prints and distributes banknotes and coins, ensuring a sufficient supply of currency to meet the economy’s needs.
Monetary Policy Regulation
The RBI formulates and implements monetary policy to control the supply of money in the economy. This involves adjusting interest rates and using other tools to influence inflation, control liquidity, and promote economic growth. For example:
- Repo Rate: The rate at which commercial banks borrow money from the RBI. Adjusting this rate can influence the amount of money in the economy.
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): The percentage of a bank’s total deposits that must be kept in reserve with the RBI. Changing the CRR affects the amount of funds banks have available to lend.
Inflation Control
One of the primary responsibilities of the RBI is to maintain price stability. By regulating the money supply and interest rates, the RBI aims to keep inflation within a target range. This helps maintain the purchasing power of the fiat currency.
Foreign Exchange Management
The RBI manages India’s foreign exchange reserves and oversees the foreign exchange market to stabilise the Indian rupee. It includes exchange foreign currencies to maintain a balanced exchange rate, which is crucial for international trade and investment.
Also Read: Forex Trading
Banking Regulation and Supervision
The RBI regulates and supervises the banking sector including setting guidelines for bank operations, monitoring their financial health, and taking corrective actions when necessary.
Financial Inclusion
The RBI promotes financial inclusion by ensuring that banking services are accessible to all sections of society. This includes initiatives to bring banking services to rural and underserved areas, encouraging the use of digital payments, and supporting microfinance institutions.
Currency Management and Counterfeit Detection
The RBI ensures the integrity of the currency by executing measures to detect and prevent counterfeiting. It regularly updates the design and security features of banknotes to stay ahead of counterfeiters.

Advantages of Fiat Currency
Let’s take at some benefits of exchanging businesses via fiat money:
- Economic Stability: Governments can manage the supply of money to stabilise the economy.
- Convenience: Fiat money is easy to carry and use for transactions.
- Flexibility: Central banks can use monetary policy to control economic factors such as inflation and unemployment.
Disadvantages of Fiat Currency
Here are few setbacks or limitations of fiat money for an economy:
- Inflation Risk: Excessive printing of fiat money can lead to high inflation, reducing the currency’s value.
- Government Dependency: The value of fiat currency depends on the stability and creditworthiness of the issuing government.
- No Intrinsic Value: Unlike commodity money, fiat money doesn’t have intrinsic value, relying entirely on trust.
What are Cryptocurrencies?

Cryptocurrencies are a type of digital or virtual money that use cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (like the Indian Rupee or US Dollar), cryptocurrencies run on technology called blockchain, which is a decentralised system spread across many computers. This decentralised nature makes cryptocurrencies independent of any central authority like a bank or government.
The buzz of Bitcoin cryptocurrency has already taken the market by storm and is accepted as the currency of exchange by several companies or countries. Although these digital assets are not authorised by government authorities in countries, there are few states that have made digital currencies as fiat money. Cryptocurrencies use peer-to-peer (P2P) transactions to easily transfer these digital coins directly to each other without needing a bank or intermediary.
Examples of Cryptocurrencies
There are nearly 20,000 cryptocurrencies, however, the top 20 cryptocurrency cover approximately 90% of the entire market. Here are few examples of most-popular cryptocurrencies:
- Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most well-known cryptocurrency, created by an anonymous person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto.
- Ethereum (ETH): Known for its smart contract functionality, allowing developers to build decentralised applications.
- Ripple (XRP): Focuses on enabling real-time, cross-border payments for financial institutions.
- Litecoin (LTC): Similar to Bitcoin but with faster transaction times and a different hashing algorithm.
Are Cryptocurrencies Regulated?

Cryptocurrencies operate in a regulatory grey area, with different countries adopting varying approaches to their regulation.
The U.S. has a mixed approach to cryptocurrency regulation. Agencies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), and the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) each play a role. China has taken a stringent stance against cryptocurrencies, banning trading, mining, and initial coin offerings (ICOs). Japan is one of the most crypto-friendly countries, having legalised cryptocurrencies as a form of payment. India’s stance on cryptocurrencies has been ambiguous. The government has proposed banning private cryptocurrencies while exploring the possibility of a central bank digital currency (CBDC).
While these digital currencies are not universally regulated, the trend is towards increased oversight and regulation to protect investors, prevent illegal activities, and ensure market stability. Different countries have different approaches, ranging from outright bans to cover the market. As the cryptocurrency space continues to evolve, so too will the regulatory frameworks governing it. Understanding the regulatory environment is crucial for anyone involved in cryptocurrencies, whether as an investor, trader, or developer.
Difference Between Fiat Currency vs Cryptocurrency

Our world is increasingly digital, and money is no exception. We’ve moved from jingling coins to swiping cards, but a new contender has entered the ring: cryptocurrency. Both fiat currency and cryptocurrency allow us to buy and sell goods, but their underlying structures differ greatly.
Fiat, the traditional kind, is issued and controlled by governments. It can be physical cash or a digital record in a bank account. Cryptocurrency, on the other hand, is completely digital, and decentralised and operates on a blockchain network.
Fiat Currency vs Cryptocurrency
Here is a table that summarises the difference between fiat currency vs cryptocurrencies in simpler way:
| Feature | Fiat Currency | Cryptocurrency |
| Control | Centralised (governments/central banks) | Decentralised (blockchain network) |
| Form | Physical (cash) or Digital (bank accounts) | Digital only (stored in wallets) |
| Value | Backed by trust in issuing government and economy | Market-driven (supply, demand, sentiment) |
| Transparency | Limited transparency (money supply controlled by central banks) | Potentially more transparent (blockchain records transactions) |
| Stability | Relative stability (aimed for, but inflation can occur) | High volatility (values can fluctuate significantly) |
| Regulation | Heavily regulated by governments | Less regulated (varies depending on jurisdiction) |
| Security | Relies on traditional security measures (anti-counterfeiting) | Blockchain-based security (cryptography) |
| Transaction Fees | Generally low fees for traditional transactions | Transaction fees can vary depending on the network |
| Accessibility | Universally accepted (may require bank accounts) | Not universally accepted (limited by merchants) |
| Speed of Transactions | Can be slow for international transactions | Faster transaction times, especially for international transfers |
| Environmental Impact | Printing and transporting physical cash has an environmental cost | Crypto mining can be energy-intensive, impacting the environment |
In A Nutshell
Both fiat currency and cryptocurrency are two different types of money with unique features. Though traditional currencies are issued by the government of a country, with the widespread use of digital money and acceptance of digital currencies by major companies such as Tesla, it can be assumed that crypto money can be the new money of the modern world. Not only this, there are other aspects of digital worlds that are exchanged as money such as NFTs, metaverse assets, etc. that are seen as the new world’s properties or art. With the fundamental knowledge of the crypto world, investors can easily study the technical charts using demand-supply dynamics, support-resistance etc., staying one step ahead of other investors.
FAQs
What are the different forms of Indian Rupee?
The Rupee exists in physical forms (coins and banknotes) and digital forms (bank account balances).
How can I protect myself from cryptocurrency scams?
Be wary of unsolicited investment offers. Only invest in legitimate cryptocurrency exchanges and use digital wallet software, cold storage software, etc. to secure your wallet.
What is the Digital Rupee (e₹)?
The Digital Rupee is a central bank digital currency (CBDC) issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in digital form. It’s essentially a digital version of the Indian Rupee with the same legal tender status as physical notes and coins.
Will India create its own digital cryptocurrency in the future?
The possibility exists. The success of the e₹ pilot and the evolving regulatory area might influence the decision to create a separate digital cryptocurrency.



 Facebook
Facebook Instagram
Instagram Youtube
Youtube
