Sensex

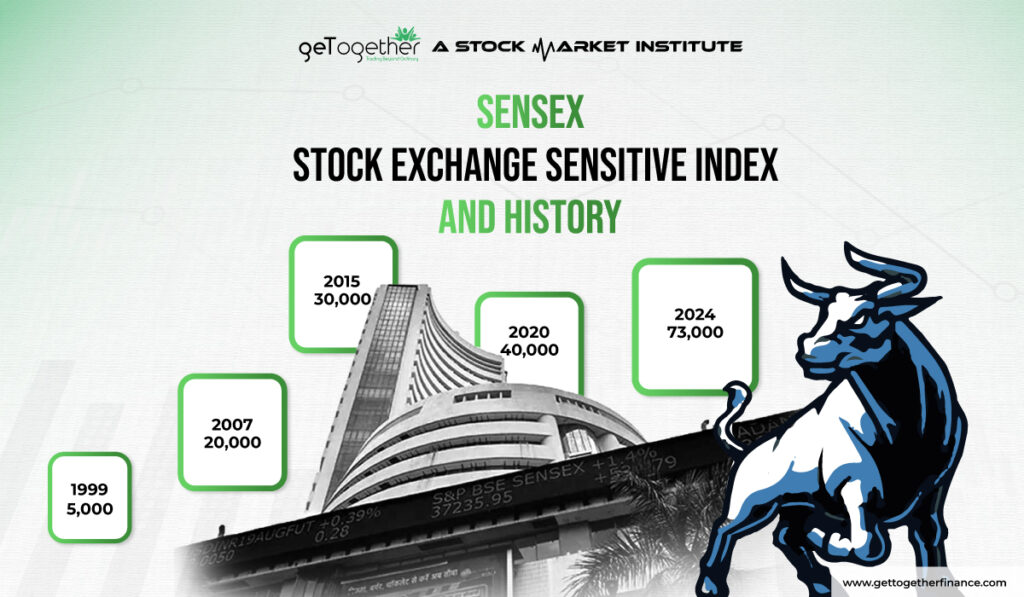
The Sensex helps in gauging the market sentiments for traders by accumulating average data from top companies listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange. The composition of Sensex involves the top 30 companies listed on BSE, it fluctuates based on the average price of all the companies of its composition. IT can be taken as a meter to gauge how well the market is performing at a particular time.
It helps in understanding the market sentiments and, if its yearly direction is going positive with good growth, it can be taken as a green signal for the growth of the Indian economy too.
When the it is going up by making new highs, it can interpreted that investors are positive about the growth of stocks, which eventually will flourish the economy. But if it goes down, it could mean trouble ahead. In this blog, we’ll explore what the Sensex is, why it’s important for Indian investors and financial health, and how it impacts everyone from investors to businesses. So, if you’re curious about one of the important meters of India’s stock market, stick around!
Table of Contents
ToggleHistory of Sensex
Before going ahead, let’s know from where it comes and what’s its history. People have built a strong rust over the BSE and its Index, Sensex. Let’s find out the reasons behind it:
Origin of Sensex
It was formed in 1986 by BSE, it was formed with the idea of an index that can gauge the overall performance of the stock market. Back then, it was launched with a base value of 100 with the top 30 companies listed on BSE. The idea behind the formulation of Sensex was to help investors with a single index to know overall market sentiments for every particular day.
Since then, investors have taken it in sync with the Indian economy, evolving into a vital indicator for investors, policymakers, and economists alike.
Evolution Over the Years
From the day it was established, it has had remarkable growth.
From its kindest start with 30 stocks on the initial day, it was going well until a sudden correction in 1996, it gave the great falls to the market by going at a year low. But, with the following year’s budget, the Sensex saw good growth. After the sudden fall, the methodology for calculating the value of Sensex also underwent several revisions to ensure its relevance and accuracy. Following, the evolution of the Indian economy, and the incorporation of technology helped it in having synchronized growth over the years and made it a reliable index for investors.
Components of Sensex

As explained above, Sensex has the top 30 companies listed on BSE, but, let’s now understand how these companies are selected to be included in Sensex.
Selection Criteria
The key factors considered while selecting the composition for it include market capitalization, liquidity, trading frequency, and sectoral diversity. Generally, the companies with a good market value of most voluminous trades are filtered out. This selection process is aimed at maintaining the accuracy and reliability of the index with a broader perspective of the market that can help investors in tracking investment trends and market sentiments.
Sectoral Representation
The Sensex strives to include a diversity of stocks to maintain a good hold over the outlook of the economy. This helps investors know that it reflects the growth of overall all sectors such as finance, information technology, consumer goods, energy, and healthcare, among others. The inclusion of stocks from all companies helps in providing investors with real-time insights into the overall growth and financial health of the economy and the market’s different segments. Further, sectoral representation also helps investors make informed decisions regarding sector-specific investments and portfolio diversification strategies.
Also Read: Stock Market Holidays
Major Companies and Their Impact
The constituents of Sensex are one of the most largest and reputed companies in India. Since their market cap is good and the majority of investors feel safe in investing in those companies, fluctuations in the price of these companies impact the volatility of Sensex. Changes in price reflect the investor sentiments and the market trends that eventually sync with it. Since these constituents have a huge impact on it, investors and traders closely monitor the performance of these major constituents to gauge the overall direction of the market and make informed investment and trading decisions.
Factors Influencing Sensex

Sensex is highly influenced by economic events and market noise. Here’s from where it gets stimulated its gets impacted:
Macroeconomic Factors: Macroeconomic factors such as GDP growth, inflation rates, interest rates, and fiscal policies of India play a huge role in influencing the it. Positive growth of macroeconomic factors signals a healthy economy, boosting investor confidence. Conversely, negative indicators can trigger panic, uncertainty, and volatility, causing the it to have negative momentum.
Global Market Trends: The Sensex is also highly influenced by global market trends and geopolitical movements. The developments in major international markets are also highly influential for it. In the current era, we have an interconnected economy, and in this global economy, events in one market can have a good effect, making it essential for investors to consider global trends when analyzing the it and making investment decisions.
Regulatory Changes and Policy Decisions: Policies are reformed in a fixed period of time and along with regulatory changes, they impact Sensex and investor sentiments heavily. The changes in interest rates, tax policies, and economic reforms can affect corporate earnings, businesses around the nation, investor sentiment, and market liquidity, consequently influencing the direction of the Sensex. Investors closely wait for policy announcements and regulatory developments like budget, fiscal policies, and others to anticipate their impact on the stock market and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
Future of Sensex

The recent outlook on Sensex can help in understanding the market is showing recovery despite having immense economic turbulence. The resistance of the market is getting stronger against all the negative events. Despite sudden falls, the overall graphs are showing an upward trajectory, showing good growth against all odds supported by factors like strong demand, bullish sentiments, excellent corporate earnings, and proactive government policies.
Following, emerging sectors like IT, renewable energy, and healthcare are on investors’ radar hence, their demand is quite increased. Following, the government’s monetary support to these sectors acted as an excellent factor in reviving the growth of the market and its diversification
If we look ahead and anticipate the future of it, the prospects for it indicate the potential for continued growth supported by structural reforms, infrastructure development, and favorable demographic trends. However, it is important to note that challenges such as geopolitical uncertainties and inflationary pressures necessities investors to follow a proper risk management plan and rely on a dynamic strategy to sway from the unexpected waves of the market. Overall, the Sensex appears good to go for sustained growth and stability, offering investors wealth for long-term wealth creation and portfolio expansion followed by a good approach.
Trading in Sensex

Although Sensex is an index, it can be traded, but not in equity, only in the FnO segment. It gives traders the liberty to trade in its derivative contracts of Futures and Options.
FnO trading in the Sensex refers to derivate trading that allows investors to anticipate and speculate on the future price movements of the it. FnO trading in Sensex started in 2000, and since then it has grown significantly with increased interest of traders. It also offers investors opportunities for hedging, speculation, and portfolio diversification against their cash market holdings. FnO derivatives instruments allow traders to leverage their positions against unfavorable market conditions and manage risks more effectively in the volatile stock market environment.
In Sensex’s FnO trading, futures contracts obligate the buyer to purchase or sell the underlying index at a pre-determined price for a certain expiry date.
Following, options contracts in Sensex provide the right but not the obligation to buy or sell the index for a specified for certain expiry date. It helps traders and investors hedge against their large holdings and ensure the losses are compensated. Options give the liberty of weekly expiry to the traders, whereas futures are traded on monthly expiry.
Many traders independently trade in FnO of Sensex to capitalize on worthwhile market opportunities.
How does it work?
Seeing the current situation, FnO trading in the Sensex continues to attract a wide range of market participants, especially day traders. The liquidity and depth of the FnO market of Sensex provide investors with a plethora of opportunities for profit-making and risk-management strategies. However, it’s essential for investors to understand the complexities of derivative trading and implement proper risk management practices to navigate the market successfully.
Limitation of Sensex

Narrow representation of the market:
- Many market critics argue that Sensex has major constituents of large cap companies, which overlooks the importance of mid-cap and small cap in the market.
- This narrow representation of companies can tamper the market perception in investors’ minds and it may not clearly reflect the diverse investment opportune ties available in the market.
Vulnerability to external shocks:
- The Sensex is highly susceptible to global events, geo-political tensions, and other factors, this makes it hard for investors to gauge market sentiments based solely on it.
- A sudden turn of events in international markets or unexpected geo events can induce volatility and sharp declines or up move in the Sensex, impacting investor confidence and portfolio values.
Alternative indices and benchmarks:
- There are other indices available in the market that are attracting investors more with sector-specific views and comprehensive value.
- These alternative indices like nifty, finnifty, banknifty, etc, offer different methodologies and sectoral compositions, catering to diverse investment strategies and preferences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Sensex is an important indicator of India’s economic health and market sentiment. From its foundation in 1986 to its transformation into a key barometer for investors and policymakers, it has passed through critical milestones, showcasing India’s resilience and dynamism. Despite its limitations, including as limited market coverage and susceptibility to external shocks, it continues to advise investors and businesses by providing insights into developing trends and investment possibilities. As we traverse the uncertainty of the future, it remains a reliable partner for those looking for growth and stability in the Indian stock market.
FAQs
What is the Sensex and why is it important?
The Sensex index measures the performance of the top 30 firms listed on the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE). It is important because it gives investors a sense of general market mood and reflects the health of the Indian economy.
How are the companies included in the Sensex selected?
The businesses on the Sensex are chosen based on a variety of criteria, including market capitalization, liquidity, trading frequency, and sectoral diversity. The top companies with the largest market value and trading activity are often chosen to assure a representative sampling of the market.
What factors influence the movements of the Sensex?
It is affected by a variety of factors, including macroeconomic indices such as GDP growth, inflation, and interest rates, global market movements, and policy actions such as regulatory changes and government initiatives. These factors can influence investor sentiment and drive fluctuations in the index.
How does the Sensex impact investors and businesses?
The Sensex is used as a benchmark for investors, guiding their investment decisions and portfolio plans. For businesses, it provides insights into market trends and investor opinion, which influence company strategies and investment choices.
What are the limitations of relying solely on the Sensex for investment decisions?
While it provides useful information, it has drawbacks such as a narrow market representation and vulnerability to external shocks. Before making an investing decision, investors should look into other indexes and benchmarks, diversify their portfolios, and undertake extensive research.



 Instagram
Instagram
