Best Options Strategy In A Sideways Market


We can easily trade when we know the direction of a particular stock and when we are familiar with some best options strategy.
Suppose if the underlying is in uptrend we can buy call or short put and if underlying is in downtrend we can buy put or sell calls.
But when we come to the sideways market its tough challenge to make money from options and a there is a high degree of risk especially in debit strategy (long call/long put).
Table of Contents
ToggleBest Options strategy in sideways market
Here are the few strategies though which we can get a decent output.
Short strangle (credit/non-directional)
Iron condor (credit/non-directional)
Short straddle (credit/non-directional)
Iron butterfly (credit/non-directional)
All of these are called as non-directional strategies which are used in sideways market.
Now a question comes in mind why 4?
All of them have different characteristics based on the market conditions.
Short Strangle and Iron Condor can be used when we know the upper and lower range in which underlying is going to be range bound based on demand and supply or support and resistance or through another technical analysis.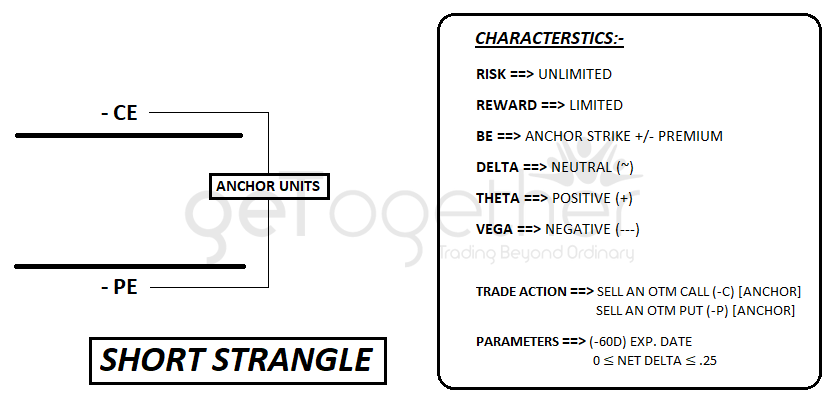
Short Strangle is used when the market is sideways and we are expecting the price to be remains range bound in upcoming days. The strategy can be initiate by selling a call and a selling a put
(Both Anchor Units). The call strike which we select to sell should be at or above the upper range, similarly the put strike should be at or below the lower range.
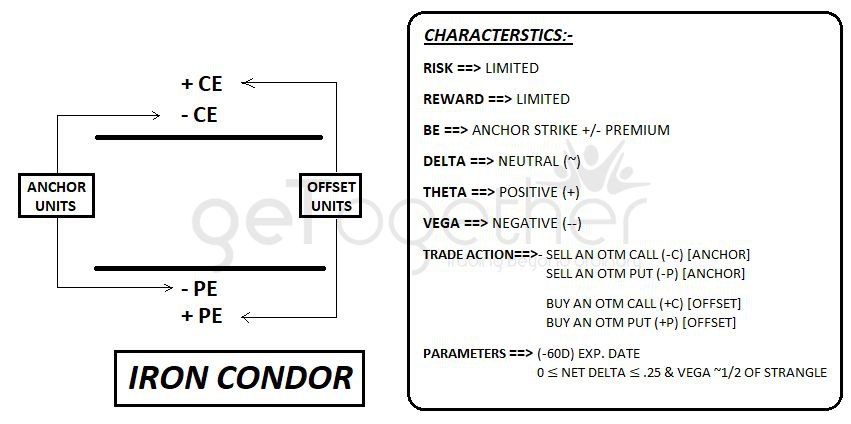
As we can see Iron Condor is slightly different from Short Strangle.
Adding two offset units into short strange will give us Iron Condor.
The major benefit for Iron Condor is now our risk is also limited.
The Offset Units strike price of long call (+CE) should be above the short call (Deep OTM), similarly strike price of long put (+PE) should be below short put (Deep OTM).
Also Read: Iron-Condor Strategy
Short Straddle and Iron Butterfly can be used when we are pretty much confident that underlying is going to be remain at around current market price only, that can be analyze through the our Trading in the Zone course or through any other technical analysis.
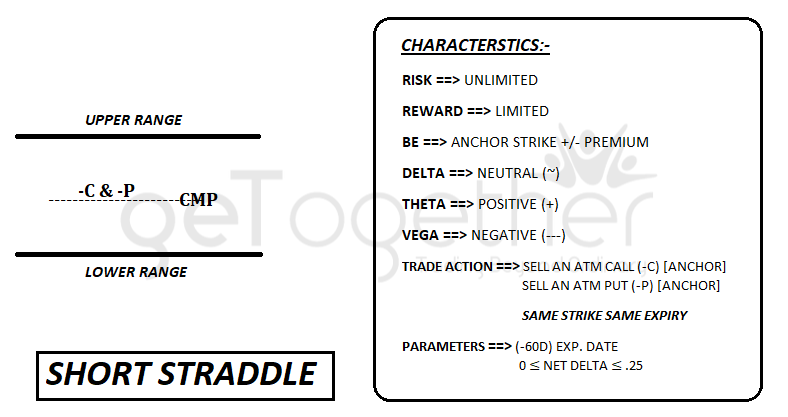
Short Straddle is used when the market is sideways and we are expecting the price to be remains around current market price only in upcoming days. The strategy can be initiate by selling a call and a selling a put (Both Anchor Units).
Both call and put should be of same strike price and same expiry
As long as price remains around current market price and as long as days pass, the strategy will count money for us.
Please not there is an unlimited risk characteristics in Short Straddle
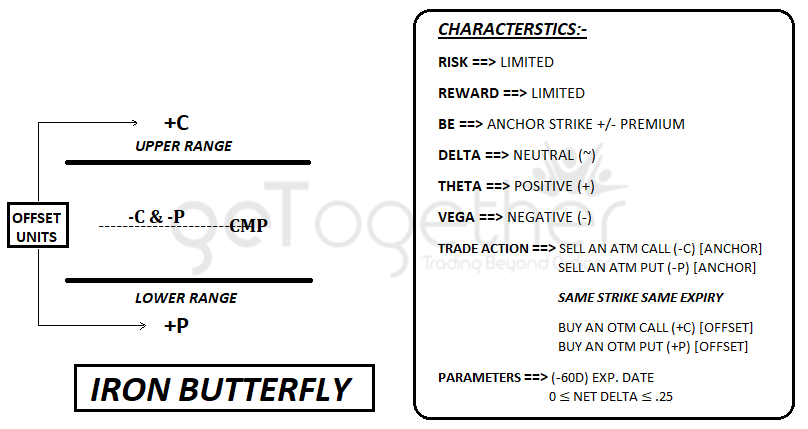
Iron Butterfly is the modified version of the Short Straddle, in which two offset units are added to prevent from unlimited risk, one is long call and one is long put.
Long call strike price should be deep OUT-THE-MONEY above the upper range, similarly long put should be deep OUT-THE-MONEY below the lower range.
Anchor unit will be same like Short Straddle (same strike and same expiry).
Which strategy is safer:-
Obviously the strategy which prevent from unlimited risk is more safe.
Iron Condor and Iron Butterfly are the safe strategy, which will prevent us not only from unexpected gap up and gap down but also prevent us from a sudden hike in implied volatility.
Best Option Trading Strategies You Need to Know
You might have come here after reading how risky options trading is and it has full potential to empty your accounts. But, take a reality check here, options trading is risky, but risk is surely manageable with a good approach and advanced knowledge. After this risk is managed, the sky is the limit in options trading. Options trading is way more advanced and exciting than just buying and selling stocks. Different options trading strategies come with the opportunity to make money in every market condition. Indeed, the one who has mastered technical analysis related to options trading has the capability to accumulate good wealth over time. There are two types of market, bullish, bearish, and sideways, and so the type of options trading strategies.
Bullish Option Strategies
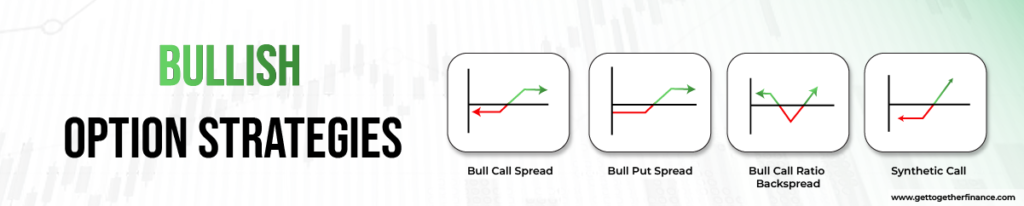
These are strategies used by a trader when they anticipate an up move in the market. It mandates the trader to thoroughly study the expected upmove and timeframe going to come. The art of catching quick-up moves brings a lot of opportunities here. Here are some different bullish options strategies that professional traders use:
Bull Call Spread
It is an excellent hedging technique used by a lot of traders out there. Here, a trader buys in-the-money(strike price lower than the current price of the underlying asset) call option and sells the out-the-money (strike price higher than the current price of the underlying asset) call option. This is done for the same underlying asset and for the same expiry date. This gives a win to the trader from both sides. But, this strategy should only be implemented when the trader is sure about the upmove in the market.
Bull Put Spread
This is used when a moderately bullish market is anticipated. Here, the trader sells an in-the-money put option and buys an out-the-money put option. The theta decay benefits highly in selling of put option. This strategy is implemented when the market has seen a good downfall a little bullish vision can be expected lately.
Bull Call Ratio Backspread
This is indeed a risky but highly rewarding options strategy. Here, the trader sells an in-the-money/at-the-money (itm / atm) call option and buys two or more call options of a specific strike price. This is all done for the same expiration date. It should be practiced when you are sure about the good upward rally in the underlying asset. As the price of the underlying asset will reach the strike price of out-the-money calls, the premium will give unwavering returns. Further, the premium of the sold call option will fall near zero, giving you double gains.
Synthetic Call
Here, the trader first purchases the stock in bulk and aims for an up move. But, to protect their invested money, they buy a put option of the same strike price as the current price of the stock. It works as an excellent insurance to the purchased stock. Even if, the stock goes in an unfavorable direction for a while, the put option compensates for the losses of stocks.
Bearish Option Trading Strategies
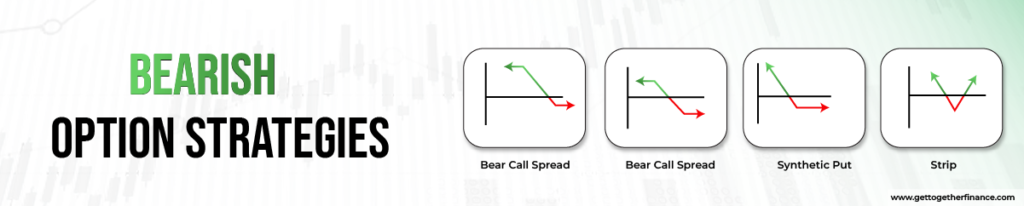
Bearish Option Trading Strategies are used by traders who anticipate a decline in the market. They aim to make money by taking short positions in the market, the more the market falls, the more their gains increase. Here are different types of bearish option strategies used by technical traders:
Bear Call Spread
Here the trader sells an in-the-money call option and buys an out-the-money call option for a higher strike price. It gives the seller a limited gain or reward opportunity due to theta or time decay. The gains are guaranteed here if the stock declines or even remains steady. Both the call options are of the same underlying asset and of expiry date.
Bear Put Spread
In a bear put spread, the trader again benefits from a decline in the market. Here the the trader buys out-the-money put options and sells in-the-money put options. The gain here is also limited, but the gains are guaranteed if you have forecasted a decline in the market.
Strip
This is the market-neutral strategy that involves holding long positions of both call and put for the same strike (at-the-money) price at the same expiry date. The profits are made when the market moves either side. But the profits are doubled when the market moves to the downside rather than to the upside. Hence, it is a bearish option strategy.
Synthetic Put
Similar to synthetic call, it is used to protect the short position the trader has taken in the stock. But, to protect their invested money, they buy a call option at an at-the-money price. It works as an excellent insurance to the short position. Even if, the stock goes in an unfavorable direction for a while, the call option compensates for the losses of stocks.
Neutral Option Trading Strategies
Neutral option trading strategies are employed by investors who anticipate little to no significant price movement in the underlying asset. These strategies aim to profit from low volatility and can be implemented when the investor expects the price of the underlying security to remain within a specific range.
Long Straddles and Short Straddles
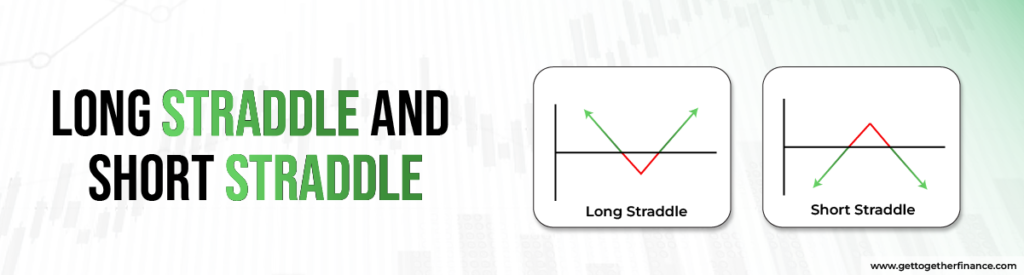
- Long Straddle:
- Definition: A long straddle is an options trading strategy where an investor simultaneously purchases a call option and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date for the same underlying asset.
- Objective: The goal of a long straddle is to profit from significant price movement in the underlying asset. This strategy is used when the investor expects a substantial move in either direction but is uncertain about the direction.
- Risk and Reward: The risk is limited to the total premium paid for both options. The potential reward is theoretically unlimited if the underlying asset makes a significant move in either direction, covering the combined premiums paid for the call and put options.
- Short Straddle:
- Definition: A short straddle is an options trading strategy where an investor sells both a call option and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date for the same underlying asset.
- Objective: The goal of a short straddle is to profit from low volatility, with the expectation that the underlying asset will remain relatively stable and not experience significant price movement.
- Risk and Reward: The risk in a short straddle is theoretically unlimited if the underlying asset experiences a substantial price movement in either direction. The potential reward is limited to the combined premiums received for selling the call and put options.
Long Strangle and Short Strangle
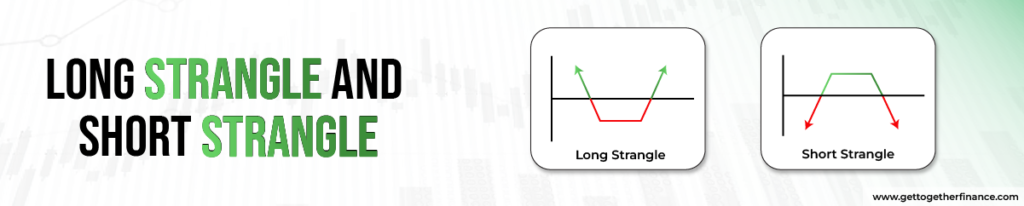
- Long Strangle:
- Definition: A long strangle is an options trading strategy where an investor simultaneously purchases an out-of-the-money (OTM) call option and an out-of-the-money put option for the same underlying asset. Both options have the same expiration date, but their strike prices are different.
- Objective: The goal of a long strangle is to profit from a significant price movement in the underlying asset, regardless of the direction. This strategy is employed when the investor anticipates a substantial move but is uncertain about whether it will be upward or downward.
- Risk and Reward: The risk is limited to the total premium paid for both options. The potential reward is theoretically unlimited if the underlying asset experiences a significant price movement in either direction, surpassing the combined premiums paid for the call and put options.
- Short Strangle:
- Definition: A short strangle is an options trading strategy where an investor sells an out-of-the-money (OTM) call option and an out-of-the-money put option for the same underlying asset, with both options sharing the same expiration date.
- Objective: The goal of a short strangle is to profit from low volatility, with the expectation that the underlying asset will remain within a certain price range until the options expire.
- Risk and Reward: The risk is theoretically unlimited if the underlying asset experiences a substantial price movement in either direction. The potential reward is limited to the combined premiums received for selling the call and put options. However, it’s important to note that the risk in a short strangle is typically considered higher than the potential reward.
Summary:-
Since all are the credit strategy. As long as market will remain sideways, these strategies are going to count money for us. But the implementation of these strategies should be based on Implied Volatility.
If implied Volatility is extremely high Short Strangle and Short Straddle are the best strategy.
If implied volatility is high but not super inflated then Iron Condor is the best strategy. If implied volatility is neither high nor low means it is mid-point (68 % time according to 1 STD) then Iron Butterfly is the best strategy.
If you like this post, then I’d really love it if you can share it on
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best option strategy for beginners?
Considering their straightforward technique and low risk, synthetic calls are frequently seen as a smart option strategy for newcomers. This approach entails owning a stock and selling call options against it or vice-versa in short positions. Selling a call generates income while limiting possible losses if the stock falls. It takes a conservative approach to options, allowing newcomers to get experience in options trading while also providing a built-in hedge. Before implementing this technique, however, it is critical to thoroughly grasp the risk factors and the underlying stock.
How can I determine the best option strategy for a specific stock?
Assess your market forecast, risk tolerance, and intended profit potential to establish the optimum option strategy for a certain stock. Consider implied volatility, stock volatility, and the time horizon. Covered calls, protected puts, and spreads may be appropriate in different conditions, so adapt the strategy to your objectives and risk profile. Learn the art of demand and supply in the stock market first, and then start trading with cash. Once you’ve mastered cash trading in stocks, you can move on to the world of options.
What are some popular option strategies for income generation?
Some popular option strategies are synthetic put, synthetic call, bull call spread, and put spread. These strategies focus more on protecting your money.
What’s the difference between bullish and bearish option strategies?
Bullish option strategies are utilised when an investor expects the underlying asset’s price to rise. Among these methods are buying calls, bull call spreads, and cash-secured puts. They benefit from price increases.
Bearish option methods are used when an investor believes the underlying asset’s price will fall. Buying puts, bear put spreads, and selling calls are some examples. These tactics seek to profit from price declines.
How do I manage risk when using option strategies?
Risk management in option strategies entails numerous fundamental approaches. Initially, use proper position sizing, restricting your investment in every single trade to a small percentage of your whole portfolio. Diversification is essential—spread your investments across several assets or methods to reduce the impact of a single position’s bad moves. Use stop-loss orders to exit a transaction automatically if it reaches a predefined loss level. Continuously watch the market and alter positions as needed, taking into account changes in implied volatility and possible news. Before joining any trade, educate yourself thoroughly, understand the hazards of each approach, and always examine the risk-reward ratio.
Can you recommend the best option strategy for a volatile market?
In a noisy or volatile market, option strategies such as long straddles or strangles might be advantageous. These entail purchasing a call and a put on the same asset, with the expectation of big price swings. Another strategy is to use iron condors, which combine bull and bear spreads to profit from a range-bound market. These techniques seek to profit from greater volatility while minimising potential losses from price movements that are unforeseen.
What is the best strategy for options trading during earnings season?
During earnings season, when stock prices might fluctuate significantly, option methods such as straddles or strangles can be effective. These techniques entail purchasing a call option and a put option on the same asset with the same expiration date. Following a company’s results announcement, this strategy anticipates big price moves in either direction. Traders can benefit from increased volatility by attempting to profit from the stock’s significant price fluctuation following earnings. However, before using these techniques during earnings season, it is critical to evaluate implied volatility levels and option costs.
How do I choose the best time frame for my option strategy?
The best time period for an option strategy is determined by a number of factors, including market conditions, your investing objectives, and the volatility of the underlying asset. Shorter time frames, such as weekly or monthly options, suit traders looking for swift market swings, particularly during events such as earnings releases. Long-term strategies, which use options that expire in several months, serve to investors who are focused on underlying trends and anticipate more gradual price adjustments. Consider the underlying asset’s volatility: higher volatility frequently favours shorter time frames for strategies such as straddles, whilst lower volatility may fit better with longer-term strategies such as spread calls. Finally, to make an informed decision, match your time frame with your risk tolerance, market outlook, and strategy particular requirements.
What are the key factors to consider when selecting the best option strategy?
Consider critical elements such as market conditions, underlying asset volatility, time horizon, and risk tolerance when selecting an option strategy. To choose a suitable strategy, consider your stock or market outlook—bullish, bearish, or neutral. Examine implied volatility levels and how they affect option price. Consider the intricacy, possible profit, and risk exposure of the plan. Finally, align your selected technique to your financial goals, whether you want to generate revenue, speculate on market swings, or hedge against future losses.
What are the pros and cons of using options strategies for hedging?
The ability to restrict possible losses and provide downside protection for a fraction of the cost of owning the underlying asset is one of the benefits of using options for hedging. Options enable hedges to be tailored to specific risk levels. However, the disadvantages include the cost of purchasing options and the chance of expiration without exercise, which could result in a loss of premium. Effective hedging requires precise timing and strategy selection.
CATEGORIES



 Facebook
Facebook Instagram
Instagram Youtube
Youtube
