How to do Swing Trading: Strategies, Techniques, and Tips
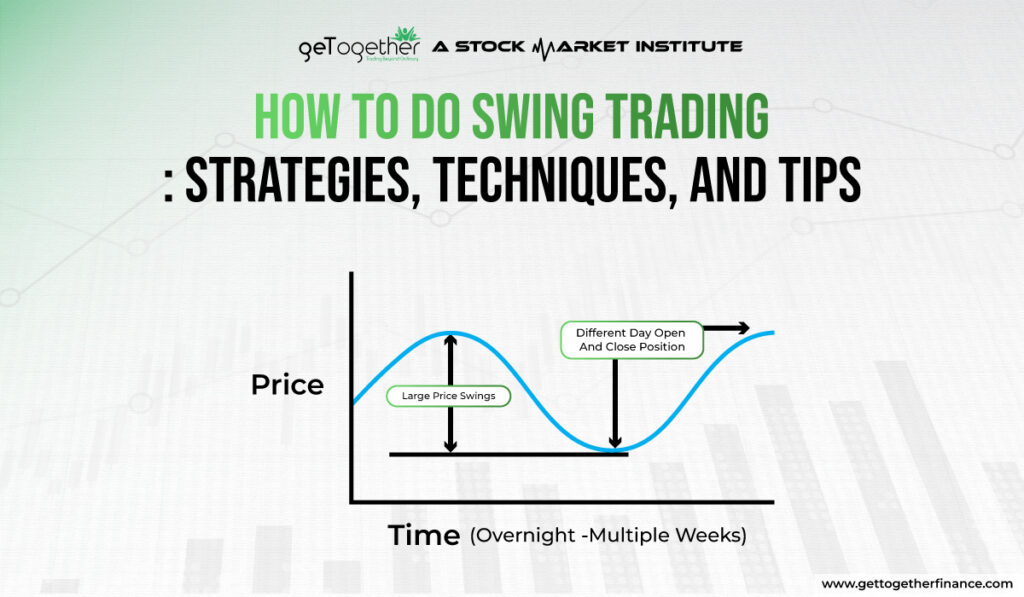
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview
The hustle of the market often forces a choice between short-term bursts and long-term commitments. Swing traders, however, have discovered a sweet spot in the middle. Swing trading stocks allows them to enter the market at opportune moments, ride profitable trends for days or weeks, and then exit strategically, capturing gains without getting caught up in the day-to-day frenzy or the multi-year wait.
This e-guide will explore the basic fundamentals of swing trading, including its definitions, advantages, and risks associated with it. It will further dive deep into how to swing trade and best swing trading stocks while establishing the difference between long-term and day trading.
So without further ado, let’s get started.
What is Swing Trading
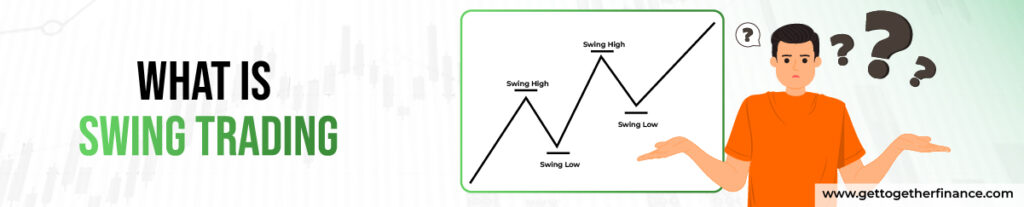
Swing trading involves holding positions in securities, such as swing trading stocks, currencies, or commodities, for a period ranging from several days to a few weeks. Swing traders aim to “swing” with the short-term momentum of the market. It aims to make money on price fluctuations within an identified trend. Unlike day traders who open and close positions within a single trading day, swing traders hold positions for a longer duration.
The goal of swing trading is to profit by buying a stock or option at a low price and selling it at a higher price later. However, just like baking a cake, there’s a risk of it not turning out as expected. Sometimes the price moves against you, resulting in a loss instead of a gain.
This can be challenging for beginners. Losing money, especially early on, can be discouraging. While it offers a way to make money in the stock market, it’s not without its difficulties. It requires practice, patience, and the ability to handle the market’s ups and downs.
Advantages & Disadvantage of Swing Trading

Swing trading offers a unique approach to profiting from the market, but like any strategy, it comes with its own set of pros and cons. Here’s a breakdown of the key advantages and disadvantages to consider before leaping for investment in swing trading stocks:
Advantages of Swing Trading
Profit Potential
Compared to day trading,it allows you to capture potentially larger profits by capitalising on broader market movements over several days or weeks.
Time Flexibility
Swing traders enjoy greater flexibility than their day trading counterparts. Investors can hold the positions for extended periods, requiring less time actively monitoring the market throughout the day.
Reduced Emotional Trading
By focusing on trends over shorter-term fluctuations, swing traders can help reduce the emotional impulse trading that can fog the minds of day traders.
Also Read: Position Trading
Disadvantages of Swing Trading
Market Volatility Dependence
The success of swing trading is linked to market volatility. In calmer markets, swing traders might encounter fewer lucrative opportunities.
Overnight and Weekend Risk
Unlike day traders who typically close positions before the market closes, swing traders are exposed to the risk of price gaps occurring overnight or over weekends, potentially leading to unexpected losses.
Discipline Required
It is crucial to adhere to a well-defined trading plan and manage emotions for swing traders’ success. The extended holding periods can be tempting to deviate from the plan, leading to potential losses.
Let’s take a brief looks at the pros and cons of swing trading stocks in a simplified way:
| Feature | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Profit Potential | Higher potential | Lower than successful day trading |
| Time Commitment | More flexible | Less than long-term investing |
| Emotional Trading | Less impulsive decisions | Discipline still required |
| Market Dependence | Thrives in volatility | Fewer opportunities in calm markets |
| Overnight/Weekend Risk | Overnight/weekend gaps | Day traders avoid this risk |
| Learning Curve | Technical analysis needed | Less demanding on fundamentals |
| Risk Management | Essential to implement risk management strategies like stop-loss orders. | Improper risk management can lead to significant losses. |
How to do Swing Trading: A Step-by-Step Guide

Swing trading is a popular strategy for those looking to profit from short to medium-term market movements. Here’s a simple, step-by-step guide on how to swing trade.
Understand Swing Trading Basics
First step to learn how to swing trade is to get yourself familiarised with the concept of swing trading. This strategy involves buying swing trading stocks or options at a low price and selling them at a higher price within a few days or weeks. The goal is to capitalize on price swings in the market.
Set Up Your Trading Account
To start swing trading, you’ll need a trading account. Choose a reputable brokerage that offers low transaction fees and a user-friendly platform. Make sure the platform provides the necessary tools for technical analysis.
Learn Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is crucial for swing trading. Investors need to learn to read charts, understand indicators like demand-supply dynamics, moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), or any theory of your choice. Traders can also with conventional technical patterns and recognize such as head and shoulders or cup and handle to forecast the future price action. This will help you identify potential entry and exit points.
Develop a Trading Plan
Create a trading plan that outlines your goals, risk tolerance, and strategies. Decide how much capital you’re willing to invest and how much you’re willing to risk on each trade. A solid plan is essential to face success in this region most of the time.
To create a well developed trading plan, maintain your watch list by selecting the best stocks with the help of top down approach and take proper measures to manage the risk. Initially 1% risk on capital per trade can be allowed which can be increased after gaining experience. In your trading plan, your risk is calculated by: Quantity = Risk per trade / (Entry – Stop Loss)
So, if you have 1 lakh capital then risk is Rs 1000 per trade, suppose the difference of entry and stop loss is Rs 10, according to this you can purchase 100 shares. This would be the best trading plan as a beginner which can be deeply understood from the below video.
Identify Potential Trades
Use technical analysis to identify swing trading stocks or options with strong potential for price swings. Look for securities that are about to break out of a consolidation phase or those that have just experienced a pullback.
Execute Your Trades
When you find a good opportunity, place your buy order. Be sure to set a stop-loss order to minimise potential losses if the trade goes against you. This is a crucial part of how to swing trade effectively.
Monitor Your Trades
Keep an eye on your trades, but avoid obsessively watching the market. Check in regularly to see if the price is moving as expected. Adjust your stop-loss orders if necessary to protect your gains.
Exit Your Trades
When the stock or option reaches your target price, sell it to lock in your profits. Alternatively, if the trade isn’t performing as expected and hits your stop-loss, exit the trade to limit your losses.
Review and Learn
After exiting a trade, review your decisions and the outcome. Analyse what worked and what didn’t. This will help you refine your strategy and improve your swing trading skills over time.
Stay Informed
Keep up with market news, trends, and updates. Staying informed will help you make better trading decisions and adapt to changing market conditions.
By following these steps on how to swing trade, you can take advantage of market fluctuations and potentially make significant profits. Remember, practice and patience are key to mastering swing trading.
Swing trading vs. Day trading
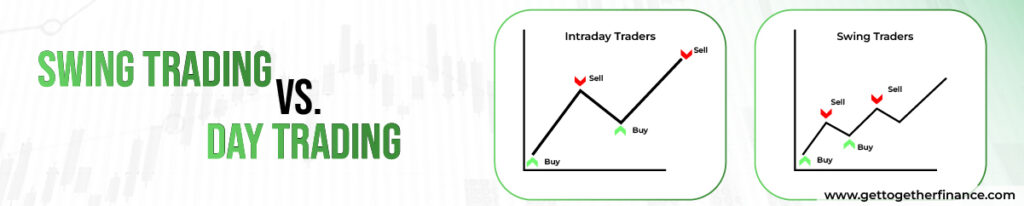
Both swing trading and day trading capitalise on short-term market movements, but they cater to different preferences. Swing trading stocks offer more flexibility, with positions held for days or weeks. This allows for profiting from broader trends using technical analysis. However, it comes with overnight and weekend risks.
Day trading, however, requires constant monitoring and quick decisions to capture fleeting intraday opportunities. It carries less overnight risk but contains higher transaction costs and the potential for emotional decisions, especially in the volatile markets.
Here let’s take a brief look at the differences between swing trading and day trading:
| Feature | Swing Trading | Day Trading |
| Time Commitment | More flexible – positions held for days/weeks | Less flexible – positions opened/closed within a day |
| Trading Strategy | Focuses on trends & longer-term price movements | Utilises short-term technical indicators & strategies |
| Risk Profile | Potentially larger profits, but exposed to overnight/weekend risk | Lower overnight risk, but higher transaction costs & emotional trading risk |
| Market Monitoring | Less frequent monitoring needed | Constant monitoring & quick reactions required |
| Suitability | Moderate risk tolerance & limited time | High risk tolerance & significant time commitment |
Swing trading vs. long-term position trading

Swing trading and long-term position trading cater to opposite ends of the investment timeline. Swing traders hold positions for days or weeks, aiming to capture profits from short-term trends using technical analysis. They thrive in volatile markets and accept moderate risk for potentially larger gains than buy-and-hold strategies.
Long-term traders, on the other hand, hold stocks for months or years, focusing on a company’s long-term potential through technical and fundamental analysis. This lower-risk approach aims to ride out market fluctuations and build wealth over an extended timeframe. Ultimately, the best choice depends on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and available time for active market monitoring.
Here is a simplified way to demonstrate the difference between both swing trading and long-term position trading:
| Feature | Swing Trading | Long-Term Position Trading |
| Time Horizon | Days or weeks | Months, years, or decades |
| Investment Focus | Short-term trends | Long-term company growth |
| Analysis | Technical analysis | Fundamental analysis |
| Market Volatility | Thrives in volatility | Focuses on long-term fundamentals |
| Risk & Reward | Moderate risk, potentially higher profits | Lower risk, potentially lower rewards |
| Monitoring | Requires some active monitoring | Less frequent monitoring needed |
Conclusion
Swing trading presents a unique opportunity for market participants seeking to potentially capture profits from price movements beyond the world of day trading but with a shorter time horizon than long-term investing. However, it’s crucial to acknowledge the inherent risks involved and approach this strategy with a cautious and well-informed perspective. An investor needs to learn comprehensive information such as definitions, merits, risks, and how to swing trade, before leaping for investing in swing trading stocks. Remember, akin to other trading options, this technique also hinges on a strong foundation in technical analysis, effective risk management, and unwavering discipline.
FAQs
Do Swing Traders Use Technical Analysis?
Yes, swing traders heavily depend on technical analysis to spot potential trades. They use demand-supply dynamics, charts, indicators, and patterns to predict price movements and determine the best entry and exit points for trades.
Is Swing Trading Risky?
Yes, swing trading carries risks, just like any trading strategy. The market can be unpredictable, and prices may not move as expected, potentially leading to losses. Proper risk management, such as using stop-loss orders, can help mitigate some of these risks.
How Much Money Can I Make Swing Trading?
The amount of money you can make swing trading varies widely and depends on factors like your initial investment, trading skill, market conditions, and risk management. While some traders achieve significant profits, others may experience losses, especially when starting out.
Can You Swing Trade With Any Stock or Option?
Yes, you can swing trade with most stocks or options. However, it’s generally better to choose securities with high liquidity and volatility, as these are more likely to experience the price swings that swing traders aim to profit from.



 Facebook
Facebook Instagram
Instagram Youtube
Youtube
